TECH
Electronic Data Processing Meaning: Unlocking Powerful Benefits

what is electronic data processing? In the simplest terms, it’s the use of computers and other electronic devices to collect, manipulate, store, and distribute data. EDP automates what used to be manual, paper-based tasks—think payroll, inventory, billing, and more.
But in 2025, EDP is much more than just automation. It’s the backbone of digital transformation, enabling real-time analytics, secure transactions, and seamless customer experiences. If you’ve ever checked your bank balance online or received a personalized marketing email, you’ve benefited from electronic data processing.
A recent tweet summed it up perfectly:
“EDP is like the invisible engine that keeps every business running. You don’t see it, but you’d notice if it stopped.”
Electronic Data Processing Meaning: A Deeper Dive
Let’s get a bit more technical. The electronic data processing meaning covers all the steps involved in handling data electronically:
- Input: Data is collected from various sources—forms, sensors, transactions, etc.
- Processing: Computers perform calculations, sort, filter, and analyze the data.
- Storage: Processed data is saved in databases or cloud storage for future use.
- Output: Results are presented as reports, dashboards, or automated actions.
This cycle happens millions of times a day in every industry you can imagine.
What Is EDP? The Evolution from Paper to Pixels
If you’re still asking, what is EDP, here’s a quick history lesson. Decades ago, businesses relied on clerks to manually record and process data. It was slow, error-prone, and expensive. The arrival of electronic data processing in the mid-20th century changed everything.
Early EDP systems used punch cards and mainframes. Today, we have cloud-based platforms, AI-driven analytics, and real-time database processing. The core idea remains the same: use technology to make data work for you.
Database Processing: The Heart of EDP
You can’t talk about electronic data processing meaning without mentioning database processing. Databases are where most of the world’s data lives—customer records, sales transactions, inventory lists, and more.
Modern EDP systems use powerful database engines to:
- Store massive amounts of data securely
- Retrieve information in milliseconds
- Support complex queries and analytics
- Enable multi-user access without conflicts
Whether you’re running a small online store or a multinational corporation, database processing is what keeps your data organized and accessible.
Real-Life Example: EDP in Action
Let’s say you order a pair of shoes online. Here’s how EDP works behind the scenes:
- Your order details are entered into the retailer’s system (input).
- The system checks inventory, processes payment, and updates your order status (processing).
- Your order info is stored in a database for tracking and future marketing (storage).
- You receive a confirmation email and shipping updates (output).
All of this happens in seconds, thanks to electronic data processing.
Why Electronic Data Processing Matters in 2025
In today’s hyper-connected world, EDP is more important than ever. Here’s why:
- Speed: Businesses can process transactions and respond to customers instantly.
- Accuracy: Automated systems reduce human error.
- Scalability: EDP handles everything from a handful of records to billions of transactions.
- Security: Modern EDP systems include encryption, access controls, and audit trails.
If you’re in business, healthcare, education, or government, EDP is part of your daily life—even if you don’t realize it.
What Is Electronic Data Processing in Different Industries?
Retail
EDP powers everything from point-of-sale systems to inventory management and personalized marketing.
Healthcare
Hospitals use EDP for patient records, billing, and appointment scheduling—improving care and efficiency.
Finance
Banks rely on EDP for transactions, fraud detection, and regulatory compliance.
Manufacturing
EDP tracks production, manages supply chains, and supports quality control.
No matter the industry, electronic data processing meaning is all about making data useful, actionable, and secure.
The Building Blocks of EDP: Hardware, Software, and People
EDP isn’t just about computers. It’s a combination of:
- Hardware: Servers, storage devices, networks, and user devices.
- Software: Operating systems, database management systems, analytics tools, and custom applications.
- People: IT professionals, data analysts, and end-users who interact with the system.
In 2025, cloud computing and AI are making EDP even more powerful and accessible.
Database Processing: How It Works
Let’s zoom in on database processing. Here’s what happens under the hood:
- Data Entry: Information is entered via forms, APIs, or automated feeds.
- Validation: The system checks for errors or inconsistencies.
- Storage: Data is saved in structured tables, often in relational databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or cloud platforms like AWS and Azure.
- Retrieval: Users or applications request data using queries.
- Reporting: The system generates reports, dashboards, or triggers automated actions.
Efficient database processing is what makes EDP systems fast, reliable, and scalable.
What Is EDP Security? Risks and Best Practices
With great power comes great responsibility. EDP systems handle sensitive data—personal info, financial records, trade secrets. That’s why security is a top priority.
Risks:
- Data breaches
- Ransomware attacks
- Insider threats
- Compliance violations
Best Practices:
- Use strong encryption for data at rest and in transit
- Implement role-based access controls
- Regularly update and patch systems
- Monitor for suspicious activity
A data breach can cost millions and damage your reputation. In 2025, robust EDP security is non-negotiable.
Pros and Cons of Electronic Data Processing
Pros
- Efficiency: Automates repetitive tasks, freeing up human talent for higher-level work.
- Accuracy: Reduces errors and improves data quality.
- Speed: Processes large volumes of data in seconds.
- Scalability: Grows with your business needs.
Cons
- Cost: Initial setup and maintenance can be expensive.
- Complexity: Requires skilled IT staff and ongoing training.
- Security Risks: Attracts cybercriminals if not properly protected.
- Dependence on Technology: System failures can disrupt operations.
Understanding both sides helps you make informed decisions about EDP investments.
EDP in the Age of AI and Automation
In 2025, EDP is evolving fast. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are transforming how data is processed and used.
- Predictive analytics: EDP systems can forecast trends and customer behavior.
- Automation: Routine tasks like invoicing, payroll, and reporting are fully automated.
- Natural language processing: EDP systems can understand and process human language, making data entry and retrieval easier than ever.
The future of EDP is smarter, faster, and more user-friendly.
What Is Electronic Data Processing for Small Businesses?
You don’t need to be a Fortune 500 company to benefit from EDP. Cloud-based solutions make it affordable for small businesses to:
- Manage customer data
- Track sales and inventory
- Automate billing and payroll
- Generate financial reports
A small bakery owner shared, “Switching to an EDP system cut my paperwork in half and let me focus on baking, not bookkeeping.”
EDP and Compliance: Staying on the Right Side of the Law
Data privacy laws like GDPR, CCPA, and others require businesses to handle data responsibly. EDP systems help by:
- Tracking data access and changes
- Automating data retention and deletion
- Generating compliance reports
Failing to comply can result in hefty fines and legal trouble. In 2025, compliance is built into most modern EDP solutions.

What Is EDP in Education?
Schools and universities use EDP for:
- Student records and grades
- Attendance tracking
- Online learning platforms
- Resource management
EDP makes education more efficient, transparent, and accessible.
EDP and the Cloud: A Match Made in Digital Heaven
Cloud computing has revolutionized EDP. Instead of maintaining expensive on-premises servers, businesses can use cloud-based EDP solutions that offer:
- Scalability on demand
- Lower upfront costs
- Automatic updates and backups
- Global accessibility
In 2025, most new EDP systems are cloud-first, making them easier to deploy and manage.
Real-World User Experience: EDP in Action
A logistics manager recently said, “Our EDP system tracks every shipment in real time. If there’s a delay, we know instantly and can update customers. It’s a game-changer for our business.”
EDP vs. Manual Data Processing: Why the Shift?
Manual data processing is slow, error-prone, and hard to scale. EDP offers:
- Faster turnaround times
- Fewer mistakes
- Better data security
- Easier reporting and analytics
The shift to EDP is one of the biggest drivers of business efficiency in the 21st century.
What Is Electronic Data Processing in Government?
Governments use EDP for:
- Tax collection and processing
- Social services management
- Public health data tracking
- Law enforcement databases
EDP helps governments serve citizens more efficiently and transparently.
The Future of Electronic Data Processing: Trends to Watch
- Edge computing: Processing data closer to where it’s generated for faster results.
- Blockchain integration: Enhancing data security and transparency.
- Self-service analytics: Empowering non-technical users to analyze data.
- Green computing: Reducing the environmental impact of data centers.
Staying ahead of these trends will keep your business competitive.
FAQs
1. What is electronic data processing in simple terms?
Electronic data processing means using computers to collect, process, store, and output data automatically, replacing manual methods.
2. What is EDP used for in business?
EDP is used for everything from payroll and inventory to customer management and financial reporting.
3. How does database processing fit into EDP?
Database processing is a core part of EDP, allowing businesses to store, retrieve, and analyze large amounts of data quickly and securely
4. What are the risks of electronic data processing?
Risks include data breaches, system failures, and compliance violations. Using secure, up-to-date EDP systems helps minimize these risks
Final Thoughts
In 2025, knowing the electronic data processing meaning isn’t just for IT pros—it’s for anyone who wants to thrive in a data-driven world. From streamlining business operations to powering AI and automation, EDP is the digital engine behind modern life.
TECH
How a Flame Machine Transforms Any Event Stage

If you’ve ever been to a concert or sports event where a flame machine roared fire into the air, you know how unforgettable that moment feels. A flame machine doesn’t just produce heat—it produces hype, creating an atmosphere that sparks excitement and energy. But what exactly makes these fire effect machines so popular in 2025? And more importantly, how can event organizers, DJs, or production companies choose the right one?
This guide dives deep into flame machines, from stage flame machines to CO2 flame machines, rentals, safety rules, and their role in modern entertainment. Whether you’re an event planner or just curious, you’ll get everything you need to know right here.
What Is a Flame Machine?
At its core, a flame machine is a special effects device that projects real fire into the air in controlled bursts. Unlike simple lighting effects, these machines combine heat, sound, and visuals to deliver a high-impact moment.
Think of them as the ultimate pyrotechnic flame machine—only safer, customizable, and designed for entertainment venues. Most modern versions are automatic flame projectors, operated via DMX or remote controls, allowing precise timing with music, sound effects, or event cues.
Stage Flame Machine: Bringing Energy to Performances
A stage flame machine is the most common type used in concerts, festivals, and live performances. Positioned on either side of the stage, they shoot flames vertically or at angles for dramatic effects.
Modern units include LED indicators, safety sensors, and programmable bursts so they can sync perfectly with beats. This makes them a favorite for big-name DJs, touring artists, and theater productions.
Quick Tip: Pairing a stage flame machine with smoke or CO2 jets creates a layered effect, making the performance look even more explosive.
Fire Effect Machine: Why Events Can’t Resist
A fire effect machine isn’t limited to music events—it’s also seen at:
- Sports entrances (football, basketball, esports tournaments)
- Weddings and luxury parties (safe, indoor-friendly versions)
- Corporate product launches (for dramatic reveals)
- Theme parks (immersive attractions with special effects)
One event planner summed it up perfectly:
“When the flames hit at the right moment, the crowd doesn’t just watch—they feel it. That’s the magic of a fire effect machine.”
Flame Thrower Machine for Events: Extreme Impact
A flame thrower machine for events is the advanced, high-powered version. Unlike smaller indoor models, these machines shoot flames up to 10 meters high, making them ideal for outdoor concerts and stadium shows.
They’re often combined with pyrotechnics, fireworks, and laser systems to produce a synchronized spectacle. However, due to the higher risk factor, they require special licensing and certified operators.
Indoor Flame Machine: Safe Yet Stunning
Not every venue can handle massive flame bursts. That’s where the indoor flame machine comes in.
These are specially designed for small-scale events like:
- Wedding receptions
- Nightclubs and lounges
- Indoor concerts and theaters
Instead of using high-pressure fuels, many rely on ethanol-based liquids or controlled cartridges, producing shorter, safer flames while still delivering the wow factor.
Outdoor Flame Machine Rental: A Cost-Effective Option
Buying a professional flame machine can cost thousands of dollars. That’s why many event organizers look for outdoor flame machine rental services.
Rental benefits:
- Lower upfront costs
- Access to the latest models
- Trained technicians for setup and safety
- Ideal for one-off or seasonal events
Safety Note: Always confirm that the rental provider is licensed and provides insurance coverage for pyrotechnic effects.
CO2 Flame Machine: Mixing Fire and Fog
A CO2 flame machine is one of the trendiest innovations in 2025. It combines fire bursts with CO2 jets, creating a two-layered effect:
- Fire for heat and color
- CO2 for smoke and dramatic exits
This effect is hugely popular in nightclubs and DJ festivals, where CO2 clouds blast dancers while flames shoot skyward.
DJ Flame Effect: Turning Sets Into Spectacles
For DJs, a flame effect machine is like an extra band member—it makes the music visible. Imagine dropping the bass and having fire erupt in sync with the beat.
In 2025, compact flame machines are specifically designed for DJs. These units are portable, DMX-compatible, and easy to set up at clubs or small festivals.
Pro Tip: Pair your DJ flame effect with LED wristbands or laser beams for a fully immersive crowd experience.
Pyrotechnic Flame Machine: The Classic Choice
The pyrotechnic flame machine has been around for decades but remains a staple in professional event setups. Unlike CO2-based or ethanol flame machines, these rely on gas canisters or pyrotechnic fuel.
They’re capable of producing taller, hotter flames, making them ideal for:
- Stadium shows
- Outdoor festivals
- National events (parades, ceremonies)
But because they carry higher risks, only trained operators should handle them.
Automatic Flame Projector: Smart and Precise
Gone are the days of manually triggering flame bursts. In 2025, most machines are automatic flame projectors.
Features include:
- Remote or DMX control
- Pre-programmed sequences
- Music synchronization
- Real-time flame height adjustment
This automation makes flame machines safer, more reliable, and more impressive in live events.
Flame Effect Equipment: What’s Included in a Setup?
A professional flame effect equipment package usually includes:
- Flame machines/projectors
- Fuel canisters or cartridges
- CO2 or gas tanks (optional)
- Control systems (DMX, remote, or app)
- Safety barriers and extinguishers
When planning an event, always budget for installation, safety staff, and insurance in addition to equipment costs.
Safety and Regulations in 2025
Flame machines are powerful, but they’re also potentially dangerous. In 2025, regulations have become stricter. Key rules include:
- Indoor venues must use certified indoor flame machines only
- Operators require training and safety certification
- Minimum safety distances must be maintained from crowds
- Local permits are often required for outdoor flame shows
Event planners should always work with licensed technicians to ensure compliance.
Real-Life Example: Flame Machines at Sports Events
At a major football final in 2024, organizers used outdoor flame machines at player entrances. The effect was so powerful that it went viral online, with one fan tweeting:
“The flames during kickoff gave me chills—felt like the players were walking into battle.”
This example shows how flame machines do more than entertain—they create emotional moments.
The Future of Flame Machines
With AI and IoT integration, future flame machines will likely:
- Sync automatically with crowd noise levels
- Adjust flame patterns in real-time
- Use eco-friendly fuels
- Be fully programmable through mobile apps
As events become more immersive, flame machines will continue to be at the heart of multi-sensory entertainment
FAQ’s
Are flame machines safe for indoor use?
Yes, but only if you use certified indoor flame machines designed for smaller spaces with safety sensors and controlled flame height.
How much does a flame machine rental cost?
Outdoor flame machine rental typically ranges from $300–$1,000 per event, depending on the machine type and operator fees.
What’s the difference between a flame machine and a pyrotechnic flame machine?
A standard flame machine uses safer fuels and can be automated, while a pyrotechnic flame machine relies on gas or fireworks-style cartridges, producing larger flames but requiring stricter safety measures.
Can DJs use flame machines in small venues?
Yes, compact DJ flame effect machines are available for clubs and private events, but always check local fire regulations first.
Conclusion
The flame machine has evolved from a niche special effect into a mainstream event essential. From stage flame machines to CO2 flame machines and automatic flame projectors, they’ve redefined how audiences experience live entertainment.
TECH
Top Tips for Watching Safely on huramovies.to

If you’ve searched for ways to watch free movies online, chances are you’ve come across huramovies.to. For many users—whether movie lovers, students, or casual streamers—the site promises access to HD films, trending shows, and international content without subscription fees. But with that promise comes some important questions: Is it safe? Is it legal? Are there better alternatives?
This article provides an honest review of huramovies.to, explores its features, compares it to legal streaming services, and highlights safe alternatives so you can make informed choices.
What is huramovies.to?
huramovies.to is an online movie streaming platform that offers access to a wide range of films and TV shows. Users often visit it to find:
- HuraMovies HD movies for free viewing
- International content with subtitles or dubbed versions
- Popular series updates and HuraMovies new releases
- Options for free HD streaming movies without creating an account
While its catalog attracts millions of visitors, it’s important to weigh both advantages and risks before relying on it.
Features of huramovies.to
Wide Content Library
You’ll find everything from Hollywood blockbusters to indie films and Asian dramas.
No Subscription Fees
Unlike Netflix or Disney+, huramovies.to doesn’t charge a monthly fee.
Accessibility
Movies can often be streamed without creating an account.
Flexible Playback
Some versions of the site even advertise a HuraMovies download option, letting users store movies offline.
Is huramovies.to Safe to Use?
This is one of the most common questions: “Is huramovies.to safe to use for streaming?”
- Safety risks: Sites like huramovies.to often rely on ads that may contain malware or phishing attempts.
- Legal risks: Depending on your country, streaming copyrighted content without permission may be illegal.
- User experience: Many reviews mention pop-ups and redirections that can frustrate viewers.
Expert Tip: Use reputable antivirus software and consider legal alternatives for peace of mind.
huramovies.to vs Other Free Streaming Sites
| Feature | huramovies.to | Legal Platforms (e.g., Tubi, Pluto TV) |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Free | Free with ads or subscription-based |
| Content variety | Broad but pirated | Licensed, safe, high-quality |
| Subtitles/dubbed versions | Available | Available |
| Safety | Risky | Safe and secure |
| Legality | Questionable | 100% legal |
HuraMovies Alternatives in 2025
If you’re searching for huramovies.to alternatives for free streaming in 2025, here are some safe options:
- Tubi TV – Free and legal, supported by ads
- Pluto TV – Great for live TV and on-demand movies
- Crackle – Offers original series and films
- Peacock Free – Popular NBC-owned platform
- Kanopy – Free through libraries and universities
How to Access huramovies.to If It’s Blocked
Some users ask: “How to access huramovies.to if it’s blocked?”
While VPNs are commonly used, always consider the legal implications first. Many regions restrict access due to copyright violations, so exploring legal platforms is the safer route.
What Do Users Say?
In online forums and review sites, huramovies.to website review and user feedback is mixed:
- Positive: Large catalog, no fees, quick updates
- Negative: Annoying ads, safety concerns, legality issues
Expert Insights
- According to Cybersecurity Ventures, unverified streaming platforms are among the top sources of malware infections.
- The Motion Picture Association (MPA) regularly lists sites like huramovies.to under piracy watchlists.
- A study by Statista (2024) shows that over 50% of global viewers prefer ad-supported legal free platforms, indicating a shift toward safer consumption.
FAQ’s
What movies are available on huramovies.to right now?
Mostly Hollywood blockbusters, TV shows, and some international titles.
Is huramovies.to legal in my country?
It depends—many countries restrict unauthorized streaming of copyrighted films.
How to watch HD movies on huramovies.to?
The site usually streams in HD, but risks include ads, pop-ups, and potential malware.
huramovies.to latest movie releases update?
The platform updates with new films quickly, but without licensing.
huramovies.to vs other free streaming sites?
It has more titles than many sites but comes with legal and safety risks.
huramovies.to with subtitles or dubbed versions?
Yes, many films include subtitles and dubbed options for global audiences.
Conclusion
huramovies.to attracts millions with its huge library of free HD movies and shows, but it comes with legal and safety risks. For movie lovers, the smarter option is to explore legal alternatives like Tubi, Pluto TV, or Kanopy, which deliver quality content without risk.
By staying informed and prioritizing safety, you can enjoy movies online without compromising security or legality.
TECH
Soft Copy Meaning: Powerful Digital Advantage

Soft Copy Meaning refers to any document, image, or file that exists in a digital format. Unlike a hard copy, which is a physical printout you can touch and hold, a soft copy is stored electronically—on your computer, smartphone, tablet, or in the cloud.
Why does this matter? Because soft copies are the backbone of modern communication, collaboration, and record-keeping. Whether you’re emailing a contract, sharing a presentation, or submitting an assignment, you’re almost always dealing with a soft copy.
What Is a Soft Copy? The Simple Definition
What is a soft copy? It’s a digital version of any document or file. This could be:
- A Word document saved on your laptop
- A PDF emailed to your boss
- A photo stored on your phone
- An eBook downloaded to your tablet
- A spreadsheet in Google Drive
If you can view, edit, or share it electronically, it’s a soft copy.
Soft Copy vs Hard Copy: What’s the Difference?
The debate of hard copy vs soft copy is as old as the personal computer. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | Soft Copy | Hard Copy |
|---|---|---|
| Format | Digital (PDF, DOCX, JPG, etc.) | Physical (paper, printout) |
| Storage | Computer, phone, cloud | Filing cabinet, desk |
| Editing | Easy, unlimited | Requires reprinting |
| Sharing | Instant (email, cloud, USB) | Mail, hand delivery |
| Eco-friendly | Yes (no paper used) | No (uses paper/ink) |
| Security | Can be encrypted, password-protected | Can be locked away |
In 2025, soft copies are the default for most businesses, schools, and even government agencies.
Real-World Example: Soft Copy in Action
A job seeker recently shared,
“I used to print out dozens of resumes for every interview. Now, I just email a soft copy or upload it to the company’s portal. It’s faster, cheaper, and I can update it anytime.”
This shift from hard copy to soft copy is happening everywhere—from job applications to legal contracts and beyond.
Why Are Soft Copies So Popular in 2025?
Several trends have made soft copies the standard:
- Remote work: Teams need to share and edit documents from anywhere.
- Cloud storage: Services like Google Drive and Dropbox make it easy to store and access files.
- Sustainability: Reducing paper use is good for the planet and your budget.
- Speed: Soft copies can be sent, received, and updated in seconds.
Types of Soft Copies: More Than Just Documents
When people think of soft copies, they often picture Word docs or PDFs. But the term covers a wide range of digital files:
- Text files: DOCX, TXT, PDF
- Spreadsheets: XLSX, CSV, Google Sheets
- Presentations: PPTX, Google Slides
- Images: JPG, PNG, GIF
- Audio/Video: MP3, MP4, WAV
- eBooks: EPUB, MOBI, PDF
If it’s digital, it’s a soft copy.
How to Create a Soft Copy
Creating a soft copy is easier than ever:
- Type it: Use a word processor, spreadsheet, or presentation tool.
- Scan it: Use a scanner or your phone’s camera to digitize paper documents.
- Download it: Save files from the internet or cloud services.
- Convert it: Use apps to turn photos or scans into PDFs or other formats.
How to Share a Soft Copy
Sharing a soft copy is simple and fast:
- Email: Attach the file and hit send.
- Cloud link: Share a Google Drive, Dropbox, or OneDrive link.
- Messaging apps: Send files via WhatsApp, Slack, or Teams.
- USB drive: For offline sharing, copy the file to a flash drive.
Soft Copy Security: Risks and Best Practices
While soft copies are convenient, they come with security risks:
- Unauthorized access: Files can be hacked or shared without permission.
- Data loss: Accidental deletion or hardware failure can wipe out files.
- Phishing: Malicious files can be disguised as soft copies.
Best practices:
- Use strong passwords and encryption.
- Back up important files regularly.
- Be cautious with email attachments and downloads.
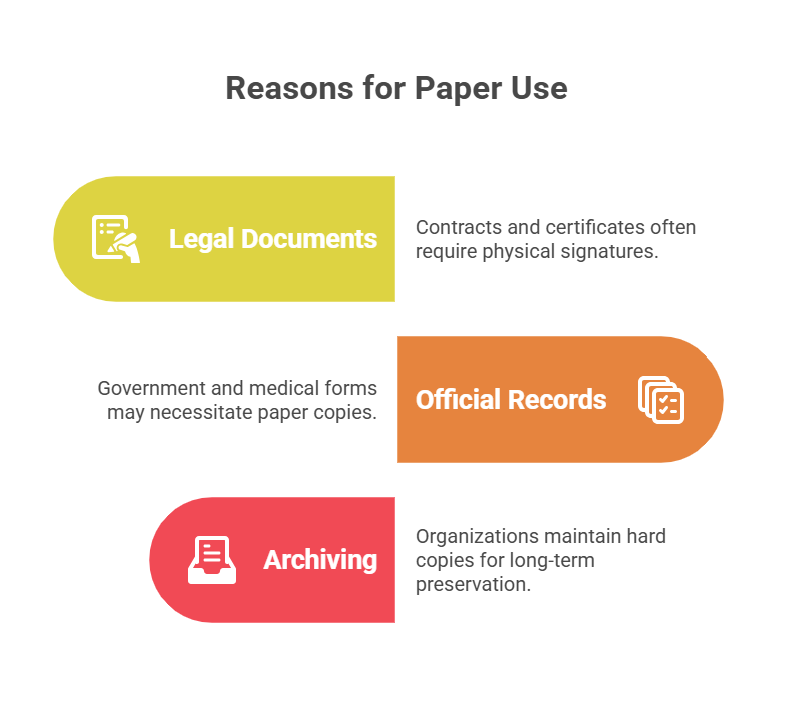
Hard Copy vs Soft Copy: When Do You Still Need Paper?
Despite the rise of soft copies, there are times when a hard copy is still required:
- Legal documents: Some contracts or certificates need a physical signature.
- Official records: Certain government or medical forms may require paper.
- Archiving: Some organizations keep hard copies for long-term storage.
But even in these cases, a soft copy is often created first and then printed as needed.
Soft Copy in Education: The New Normal
In schools and universities, soft copies have transformed learning:
- Assignments: Students submit essays and projects online.
- E-books: Textbooks are now digital, saving money and weight.
- Collaboration: Group projects happen in Google Docs or Microsoft Teams.
A teacher shared,
“I can grade assignments from my tablet, leave comments, and return soft copies instantly. No more lost papers or late submissions.”
Soft Copy in Business: Efficiency and Flexibility
Businesses rely on soft copies for:
- Contracts and proposals: E-signatures make deals faster.
- Invoices and receipts: Digital records are easier to track and audit.
- Reports and presentations: Teams can collaborate in real time.
Soft Copy in Government and Healthcare
Even traditionally paper-heavy sectors are going digital:
- E-filing: Tax returns, permits, and applications are now online.
- Medical records: Patient files are stored and shared as soft copies, improving care and reducing errors.
Pros and Cons of Soft Copies
Pros
- Easy to edit and update
- Instant sharing and collaboration
- Eco-friendly and cost-effective
- Secure (with proper precautions)
- Takes up no physical space
Cons
- Requires devices and internet
- Vulnerable to hacking or data loss
- May not be accepted for all legal purposes
- Can be accidentally deleted or overwritten
Soft Copy Meaning in 2025: The Future Is Digital
Looking ahead, soft copies will only become more important:
- AI-powered search: Instantly find any document, image, or file.
- Blockchain verification: Ensure authenticity and prevent tampering.
- Universal e-signatures: Make soft copies legally binding worldwide.
- Augmented reality: View and interact with soft copies in 3D.
FAQs
Q. What is a soft copy?
A. soft copy is a digital version of a document, image, or file that can be viewed, edited, and shared electronically
Q. How is a soft copy different from a hard copy?
A. soft copy exists in digital form (like a PDF or Word doc), while a hard copy is a physical printout on paper.
Q. Can a soft copy be printed?
A. Yes! You can print a soft copy to create a hard copy whenever needed.
Q. Are soft copies secure?
A. Soft copies can be secure if you use strong passwords, encryption, and regular backups. Always be cautious with sharing and storing sensitive files.
Real-Life Example: Soft Copy Saves the Day
A small business owner lost her laptop to a coffee spill. Luckily, all her invoices and contracts were saved as soft copies in the cloud. She accessed them from her phone and kept her business running without missing a beat.
How to Organize and Manage Soft Copies
- Use folders and clear naming conventions
- Back up files to the cloud and an external drive
- Regularly delete outdated or duplicate files
- Use document management software for large collections
Hard Copy vs Soft Copy: Which Is Better?
For most uses in 2025, soft copies win on speed, convenience, and sustainability. But for legal, archival, or official purposes, hard copies still have their place.
Final Thoughts
Understanding soft copy meaning is essential in our digital world. From job applications to medical records, soft copies are everywhere—and knowing how to create, share, and secure them is a must-have skill.
-

 BLOG5 months ago
BLOG5 months agoDitto NYT Crossword Clue Explained Clearly
-

 TECH7 months ago
TECH7 months agoSoft Copy Meaning: Powerful Digital Advantage
-

 BUSINESS8 months ago
BUSINESS8 months agoToyota vs Honda: The Battle of Bulletproof Reliability
-

 TECH8 months ago
TECH8 months agoBlue Android Phone: Single Camera Simplicity
-

 BUSINESS8 months ago
BUSINESS8 months agoUnlock Bulk Success with Amazon Business Wholesale
-

 BLOG8 months ago
BLOG8 months agoInvisible String: The Unseen Threads That Connect Us
-

 HEALTH8 months ago
HEALTH8 months agoHormone Health for Men: Signs, Solutions, and Staying Proactive
-

 FASHION8 months ago
FASHION8 months agoStyle Your Tech: Custom HP Notebook Cover Skins for a Sleek Look
