TECH
Microsoft Layoffs 2025: Powerful Impact

microsoft layoffs 2025 has been trending across news sites, social media, and professional networks. If you’re in tech, you’ve probably felt a mix of anxiety and curiosity: Why is Microsoft making cuts now? How does this compare to other big layoffs like the recent walmart layoffs or disney layoffs? And what does it mean for the future of daily job cuts in the industry?
In this in-depth guide, we’ll break down the facts, rumors, and real-life impact of the Microsoft layoffs in 2025. We’ll also explore how these changes fit into the broader landscape of tech and corporate job cuts, and what you can do if you’re affected or just want to stay informed.
The Big Picture: Why Are There Microsoft Layoffs in 2025?
Understanding the Context
Layoffs at major tech companies aren’t new, but the microsoft layoffs 2025 have caught the attention of both industry insiders and the general public. Microsoft, a company known for its stability and growth, rarely makes headlines for mass job cuts. So, what’s different this time?
The tech sector in 2025 is facing a unique set of challenges: economic uncertainty, rapid AI adoption, shifting consumer demand, and global competition. Microsoft, like many others, is restructuring to stay agile and competitive. This means letting go of some roles while investing in new areas like cloud computing, AI, and cybersecurity.
Comparing to Other Major Layoffs
It’s not just Microsoft. Walmart layoffs and disney layoffs have also made headlines this year, reflecting a broader trend of companies rethinking their workforce strategies. The rise of daily job cuts trackers and layoff news sites shows just how common these announcements have become.
“I never thought I’d see the day when Microsoft would be on the daily job cuts list. It’s a wake-up call for everyone in tech.”
Microsoft Layoff Rumors 2025: What’s Fact and What’s Fiction?
Sorting Through the Noise
Whenever a big company like Microsoft announces layoffs, rumors start flying. Some say entire departments are being axed, while others claim it’s just a minor restructuring. The truth usually lies somewhere in between.
Microsoft layoff rumors 2025 began circulating months before the official announcement. Leaked memos, anonymous posts on forums, and speculative tweets fueled anxiety among employees and job seekers alike. But as with any major news, it’s important to separate fact from fiction.
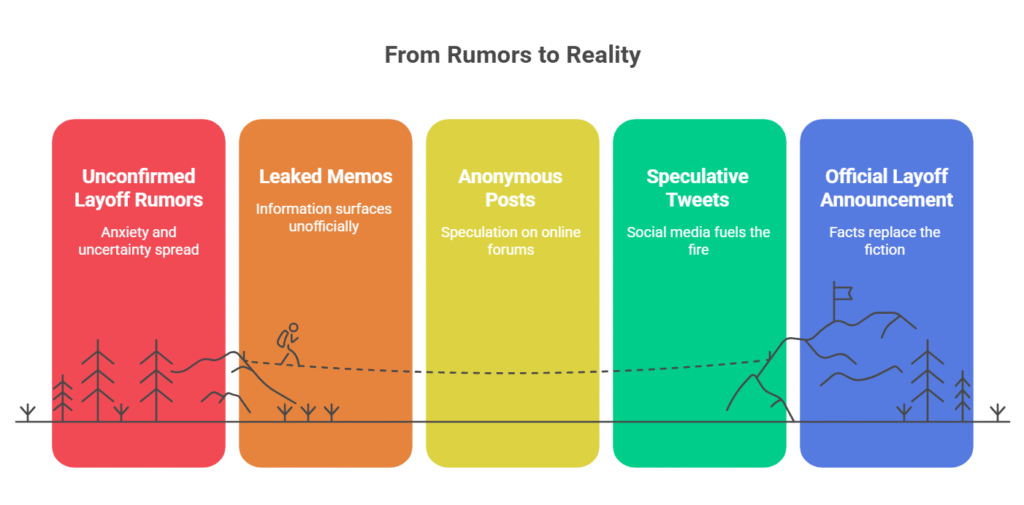
Official Statements vs. Social Media Buzz
Microsoft’s official press releases tend to be measured and vague, focusing on “strategic realignment” and “future growth.” Meanwhile, social media is full of personal stories, some true and some exaggerated. If you want the real story, look for reputable news sources and firsthand accounts.
For more on how to spot reliable information, learn more about evaluating tech news sources.
The Numbers: How Many Jobs Are Affected by Microsoft Layoffs 2025?
Breaking Down the Data
As of mid-2025, Microsoft has confirmed layoffs affecting approximately 8,000 employees worldwide. The cuts are spread across various divisions, with a focus on middle management, legacy product teams, and some support roles. Engineering and AI-focused teams have largely been spared, reflecting Microsoft’s shift toward future-facing technologies.
Regional Impact
The layoffs are not evenly distributed. U.S. offices, especially in Redmond and Silicon Valley, have seen the largest cuts. However, international offices in Europe and Asia have also been affected, particularly in sales and marketing.
How Does This Compare to Walmart and Disney Layoffs?
Walmart layoffs in 2025 have primarily targeted retail and logistics roles, while disney layoffs have hit creative and streaming divisions. Microsoft’s cuts are more focused on tech and corporate roles, but the underlying reasons—automation, cost-cutting, and strategic pivots—are similar.
Daily Job Cuts: The New Normal in 2025?
The Rise of Layoff Trackers
Sites like DailyJobCuts.com and Layoffs.fyi have become essential tools for anyone working in tech or corporate America. These platforms track layoffs in real time, offering transparency but also fueling anxiety.
Why Are Daily Job Cuts Increasing?
Several factors are driving the rise in daily job cuts:
- Automation and AI: Many routine jobs are being replaced by software and algorithms.
- Economic Uncertainty: Global events, inflation, and shifting markets make companies cautious.
- Remote Work: Some companies are consolidating offices and reducing headcount as remote work becomes the norm.
What Can Workers Do?
Stay informed, keep your skills up to date, and build a strong professional network. If you’re worried about layoffs, explore our guide to career resilience in tech.
Real-Life Example: A Microsoft Employee’s Story
“I got the email on a Tuesday morning. After 12 years at Microsoft, I was suddenly out of a job. It was a shock, but I’m grateful for the severance and support. Now I’m looking at opportunities in AI startups—something I never would have considered before.”
Stories like this are becoming more common, not just at Microsoft but across the tech industry. Layoffs are tough, but they can also open new doors.
Microsoft Layoffs 2025 vs. Previous Years
Is This the Biggest Layoff Yet?
While the microsoft layoffs 2025 are significant, they’re not the largest in the company’s history. The 2014 Nokia acquisition led to over 18,000 job cuts, and the 2020 pandemic also saw major restructuring. However, the 2025 layoffs are notable for their focus on future-proofing the company.
What’s Different This Time?
The emphasis is on shifting resources to AI, cloud, and cybersecurity. Microsoft is betting big on these areas, and employees with skills in these fields are in high demand.
Disney Layoffs, Walmart Layoffs, and the Broader Trend
Why Are So Many Big Companies Cutting Jobs?
It’s not just tech. Disney layoffs have hit creative teams as the company pivots to streaming and digital content. Walmart layoffs are a response to automation in logistics and changing consumer habits.
The common thread? Companies are adapting to a rapidly changing world, and that means tough decisions about where to invest and where to cut.
How Does Microsoft Fit In?
Microsoft’s layoffs are part of this larger trend. The company is shedding roles that no longer fit its strategic vision and doubling down on areas with the most growth potential.
The Human Side: Coping with Microsoft Layoffs 2025
Emotional Impact
Losing a job is never easy. For many, Microsoft was more than just an employer—it was a community. The layoffs have left employees feeling uncertain, anxious, and sometimes angry.
Support and Severance
Microsoft has offered severance packages, career counseling, and job placement assistance. While this helps, the transition can still be challenging.
“The hardest part wasn’t losing the job—it was saying goodbye to my team. We built something together, and now it’s over.”
Microsoft Layoff Rumors 2025: How to Stay Informed
Where to Find Reliable Information
- Official Microsoft press releases
- Reputable news outlets
- Employee forums and LinkedIn posts
- Layoff trackers like DailyJobCuts.com
Avoid relying solely on rumors or unverified social media posts. For more tips, learn more about navigating layoff news.
What Should You Do If You’re Affected by Microsoft Layoffs 2025?
Immediate Steps
- Review your severance package and benefits
- Update your resume and LinkedIn profile
- Reach out to your network for leads
- Consider upskilling or reskilling in high-demand areas like AI or cloud computing
Long-Term Strategies
- Stay positive and open to new opportunities
- Explore contract or freelance work
- Consider starting your own business or joining a startup
The Pros and Cons of Microsoft Layoffs 2025
Pros
- Allows Microsoft to invest in future technologies
- Opens up opportunities for employees to pursue new paths
- Can lead to a more agile and competitive company
Cons
- Job loss and financial uncertainty for affected workers
- Loss of institutional knowledge
- Negative impact on morale and company culture
Risks and Considerations for the Tech Industry
Will Layoffs Continue?
Most experts believe that layoffs will remain a reality in tech, especially as automation and AI continue to reshape the workforce. However, companies that invest in employee development and transparent communication are more likely to retain top talent.
How to Protect Yourself
- Keep learning and adapting
- Build a diverse skill set
- Stay connected with your professional community
FAQs
Q. Why is Microsoft laying off employees in 2025?
A. Microsoft is restructuring to focus on AI, cloud, and cybersecurity. Economic uncertainty and automation are also factors.
Q. How do Microsoft layoffs compare to Walmart layoffs and Disney layoffs?
A. Microsoft’s layoffs are focused on tech and corporate roles, while Walmart and Disney are cutting jobs in retail, logistics, and creative teams.
Q. Where can I find updates on daily job cuts and layoff rumors?
A. Check reputable news sites, official company press releases, and layoff trackers like DailyJobCuts.com. Avoid unverified rumors.
Q. What support does Microsoft offer to laid-off employees?
A. Severance packages, career counseling, and job placement assistance are typically provided
The Future of Work After Microsoft Layoffs 2025
What’s Next for Microsoft?
Despite the layoffs, Microsoft remains a leader in tech. The company is investing heavily in AI, cloud, and cybersecurity, and is likely to continue hiring in these areas.
What’s Next for Tech Workers?
The job market is shifting, but opportunities abound for those willing to adapt. Upskilling, networking, and staying informed are more important than ever.
The Bottom Line
The microsoft layoffs 2025 are a sign of the times—reflecting both the challenges and opportunities facing the tech industry. While job cuts are never easy, they can also be a catalyst for growth, innovation, and new beginnings.
TECH
Electronic Data Processing Meaning: Unlocking Powerful Benefits

what is electronic data processing? In the simplest terms, it’s the use of computers and other electronic devices to collect, manipulate, store, and distribute data. EDP automates what used to be manual, paper-based tasks—think payroll, inventory, billing, and more.
But in 2025, EDP is much more than just automation. It’s the backbone of digital transformation, enabling real-time analytics, secure transactions, and seamless customer experiences. If you’ve ever checked your bank balance online or received a personalized marketing email, you’ve benefited from electronic data processing.
A recent tweet summed it up perfectly:
“EDP is like the invisible engine that keeps every business running. You don’t see it, but you’d notice if it stopped.”
Electronic Data Processing Meaning: A Deeper Dive
Let’s get a bit more technical. The electronic data processing meaning covers all the steps involved in handling data electronically:
- Input: Data is collected from various sources—forms, sensors, transactions, etc.
- Processing: Computers perform calculations, sort, filter, and analyze the data.
- Storage: Processed data is saved in databases or cloud storage for future use.
- Output: Results are presented as reports, dashboards, or automated actions.
This cycle happens millions of times a day in every industry you can imagine.
What Is EDP? The Evolution from Paper to Pixels
If you’re still asking, what is EDP, here’s a quick history lesson. Decades ago, businesses relied on clerks to manually record and process data. It was slow, error-prone, and expensive. The arrival of electronic data processing in the mid-20th century changed everything.
Early EDP systems used punch cards and mainframes. Today, we have cloud-based platforms, AI-driven analytics, and real-time database processing. The core idea remains the same: use technology to make data work for you.
Database Processing: The Heart of EDP
You can’t talk about electronic data processing meaning without mentioning database processing. Databases are where most of the world’s data lives—customer records, sales transactions, inventory lists, and more.
Modern EDP systems use powerful database engines to:
- Store massive amounts of data securely
- Retrieve information in milliseconds
- Support complex queries and analytics
- Enable multi-user access without conflicts
Whether you’re running a small online store or a multinational corporation, database processing is what keeps your data organized and accessible.
Real-Life Example: EDP in Action
Let’s say you order a pair of shoes online. Here’s how EDP works behind the scenes:
- Your order details are entered into the retailer’s system (input).
- The system checks inventory, processes payment, and updates your order status (processing).
- Your order info is stored in a database for tracking and future marketing (storage).
- You receive a confirmation email and shipping updates (output).
All of this happens in seconds, thanks to electronic data processing.
Why Electronic Data Processing Matters in 2025
In today’s hyper-connected world, EDP is more important than ever. Here’s why:
- Speed: Businesses can process transactions and respond to customers instantly.
- Accuracy: Automated systems reduce human error.
- Scalability: EDP handles everything from a handful of records to billions of transactions.
- Security: Modern EDP systems include encryption, access controls, and audit trails.
If you’re in business, healthcare, education, or government, EDP is part of your daily life—even if you don’t realize it.
What Is Electronic Data Processing in Different Industries?
Retail
EDP powers everything from point-of-sale systems to inventory management and personalized marketing.
Healthcare
Hospitals use EDP for patient records, billing, and appointment scheduling—improving care and efficiency.
Finance
Banks rely on EDP for transactions, fraud detection, and regulatory compliance.
Manufacturing
EDP tracks production, manages supply chains, and supports quality control.
No matter the industry, electronic data processing meaning is all about making data useful, actionable, and secure.
The Building Blocks of EDP: Hardware, Software, and People
EDP isn’t just about computers. It’s a combination of:
- Hardware: Servers, storage devices, networks, and user devices.
- Software: Operating systems, database management systems, analytics tools, and custom applications.
- People: IT professionals, data analysts, and end-users who interact with the system.
In 2025, cloud computing and AI are making EDP even more powerful and accessible.
Database Processing: How It Works
Let’s zoom in on database processing. Here’s what happens under the hood:
- Data Entry: Information is entered via forms, APIs, or automated feeds.
- Validation: The system checks for errors or inconsistencies.
- Storage: Data is saved in structured tables, often in relational databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or cloud platforms like AWS and Azure.
- Retrieval: Users or applications request data using queries.
- Reporting: The system generates reports, dashboards, or triggers automated actions.
Efficient database processing is what makes EDP systems fast, reliable, and scalable.
What Is EDP Security? Risks and Best Practices
With great power comes great responsibility. EDP systems handle sensitive data—personal info, financial records, trade secrets. That’s why security is a top priority.
Risks:
- Data breaches
- Ransomware attacks
- Insider threats
- Compliance violations
Best Practices:
- Use strong encryption for data at rest and in transit
- Implement role-based access controls
- Regularly update and patch systems
- Monitor for suspicious activity
A data breach can cost millions and damage your reputation. In 2025, robust EDP security is non-negotiable.
Pros and Cons of Electronic Data Processing
Pros
- Efficiency: Automates repetitive tasks, freeing up human talent for higher-level work.
- Accuracy: Reduces errors and improves data quality.
- Speed: Processes large volumes of data in seconds.
- Scalability: Grows with your business needs.
Cons
- Cost: Initial setup and maintenance can be expensive.
- Complexity: Requires skilled IT staff and ongoing training.
- Security Risks: Attracts cybercriminals if not properly protected.
- Dependence on Technology: System failures can disrupt operations.
Understanding both sides helps you make informed decisions about EDP investments.
EDP in the Age of AI and Automation
In 2025, EDP is evolving fast. Artificial intelligence and machine learning are transforming how data is processed and used.
- Predictive analytics: EDP systems can forecast trends and customer behavior.
- Automation: Routine tasks like invoicing, payroll, and reporting are fully automated.
- Natural language processing: EDP systems can understand and process human language, making data entry and retrieval easier than ever.
The future of EDP is smarter, faster, and more user-friendly.
What Is Electronic Data Processing for Small Businesses?
You don’t need to be a Fortune 500 company to benefit from EDP. Cloud-based solutions make it affordable for small businesses to:
- Manage customer data
- Track sales and inventory
- Automate billing and payroll
- Generate financial reports
A small bakery owner shared, “Switching to an EDP system cut my paperwork in half and let me focus on baking, not bookkeeping.”
EDP and Compliance: Staying on the Right Side of the Law
Data privacy laws like GDPR, CCPA, and others require businesses to handle data responsibly. EDP systems help by:
- Tracking data access and changes
- Automating data retention and deletion
- Generating compliance reports
Failing to comply can result in hefty fines and legal trouble. In 2025, compliance is built into most modern EDP solutions.

What Is EDP in Education?
Schools and universities use EDP for:
- Student records and grades
- Attendance tracking
- Online learning platforms
- Resource management
EDP makes education more efficient, transparent, and accessible.
EDP and the Cloud: A Match Made in Digital Heaven
Cloud computing has revolutionized EDP. Instead of maintaining expensive on-premises servers, businesses can use cloud-based EDP solutions that offer:
- Scalability on demand
- Lower upfront costs
- Automatic updates and backups
- Global accessibility
In 2025, most new EDP systems are cloud-first, making them easier to deploy and manage.
Real-World User Experience: EDP in Action
A logistics manager recently said, “Our EDP system tracks every shipment in real time. If there’s a delay, we know instantly and can update customers. It’s a game-changer for our business.”
EDP vs. Manual Data Processing: Why the Shift?
Manual data processing is slow, error-prone, and hard to scale. EDP offers:
- Faster turnaround times
- Fewer mistakes
- Better data security
- Easier reporting and analytics
The shift to EDP is one of the biggest drivers of business efficiency in the 21st century.
What Is Electronic Data Processing in Government?
Governments use EDP for:
- Tax collection and processing
- Social services management
- Public health data tracking
- Law enforcement databases
EDP helps governments serve citizens more efficiently and transparently.
The Future of Electronic Data Processing: Trends to Watch
- Edge computing: Processing data closer to where it’s generated for faster results.
- Blockchain integration: Enhancing data security and transparency.
- Self-service analytics: Empowering non-technical users to analyze data.
- Green computing: Reducing the environmental impact of data centers.
Staying ahead of these trends will keep your business competitive.
FAQs
1. What is electronic data processing in simple terms?
Electronic data processing means using computers to collect, process, store, and output data automatically, replacing manual methods.
2. What is EDP used for in business?
EDP is used for everything from payroll and inventory to customer management and financial reporting.
3. How does database processing fit into EDP?
Database processing is a core part of EDP, allowing businesses to store, retrieve, and analyze large amounts of data quickly and securely
4. What are the risks of electronic data processing?
Risks include data breaches, system failures, and compliance violations. Using secure, up-to-date EDP systems helps minimize these risks
Final Thoughts
In 2025, knowing the electronic data processing meaning isn’t just for IT pros—it’s for anyone who wants to thrive in a data-driven world. From streamlining business operations to powering AI and automation, EDP is the digital engine behind modern life.
TECH
Power at a Distance: Mastering the Remote Control Excavator

Power at a Distance Remote control excavators have revolutionized construction, mining, and demolition industries by enabling operators to manage heavy machinery from safe distances. From hazardous environments to precision excavation tasks, these unmanned diggers offer enhanced safety, agile maneuverability, and cutting-edge performance. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll unpack how remote excavator systems work, explore industry use cases, discuss key technological components, and provide expert tips for maintenance and operation. Along the way, we’ll naturally weave in related industry terms—such as hydraulic control systems, telemetric feedback, operator interface design, and robotic excavation—to create depth and relevance.
What Is a Remote Control Excavator? Power at a Distance
A remote control excavator, sometimes called an unmanned digger or robotic hydraulic excavator, combines traditional excavator capabilities with advanced teleoperation. Operators use an intuitive operator interface—often with joysticks, touchscreens, or VR goggles—to manage digging, swinging, and lifting functions at arm’s length. Cameras and telemetric feedback systems relay real-time visuals and data, enabling precise earthmoving operations even when the operator cannot physically reach the machine.

Key Entities Embedded:
- Hydraulic control system
- Telemetric feedback
- Robotic excavation
- Unmanned digger
- Earthmoving operations
Why Use Remote Excavators?
Safety in Hazardous Conditions
In scenarios like mining, nuclear cleanup, or demolition site management, remote excavators prevent operators from exposure to dust, radiation, debris, or unstable structures.
Precision in Confined Spaces
Remote diggers can maneuver in tight urban settings, sewer systems, or underground tunnels where traditional operators would struggle with visibility and space constraints.
Efficiency and Labor Optimization
These machines operate longer hours under controlled conditions, reducing downtime and labor costs. They also integrate seamlessly into smart construction workflows, supporting data collection and remote diagnostics.
Core Components of a Remote Control Excavator
Teleoperation Control Unit
This crucial interface features joysticks, haptic feedback, and visual displays. Modern units incorporate VR headsets and augmented reality overlays to project terrain data, blueprints, and sensor information in real-time.
Onboard Sensors and Cameras
Robotic hydraulic excavators are equipped with omnidirectional cameras, LIDAR sensors, and pressure gauges. These elements provide the operator with situational awareness and insight into the hydraulic control system’s performance.
Communication and Safety Protocols
Whether via secure Wi-Fi, 4G/5G, or proprietary radio systems, these excavators rely on redundant links to ensure fault-tolerant operations. Emergency stop and collision avoidance sensors are standard for protecting both the machine and its surroundings.
Powertrain and Hydraulic Systems
At the heart of every excavator is its diesel engine or electric motor, powering hydraulic pumps that modulate boom, arm, bucket, and swing movements. Advanced rigs include electro-hydraulic proportional valves for smoother control.
Industry Use Cases and Applications
Mining and Quarrying
Remote-controlled shovels and excavators reduce risks in unstable rock faces, highwalls, and dusty environments. By coupling them with autonomous haul trucks, mining operations achieve a fully automated cycle—from digging to transport.
Demolition and Hazardous Material Handling
In asbestos cleanup or explosives demolition, remote excavators equipped with high-reach booms and dispersion-resistant attachments enable safe, hands-off material removal.
Urban Infrastructure Maintenance
For sewer rehabilitation, tunnel digging, or roadwork in crowded zones, mini remote excavators offer unmatched agility and precision, minimizing urban disruption and vehicular interference.
Forestry and Environmental Restoration
Equipped with specialized attachments like augers, brush cutters, or grapples, remote diggers assist in reforestation, land reclamation, and erosion control, especially in remote or steep terrain.
Choosing the Right Remote Excavator for Your Operation
Size and Operating Weight
Compact excavators (1–5 tons) are ideal for residential reno or trenching, whereas mid-to-large units (10–50 tons) support industrial scale digging and heavy lifting.
Control Interface Options
Select between portable handheld remotes, vehicle-mounted consoles, or fully immersive VR stations based on operator comfort and task complexity. Some configurations even support collaborative multi-operator control.
Communication Range and Resilience
Remote machines operate via radio, cellular, or satellite links. Evaluate signal range, latency requirements, and interference resilience for your environment.
Attachment and Integration Compatibility
From buckets to hydraulic breakers and grapples, ensure compatibility with existing attachments. In smart jobsite contexts, look for telematics platforms that integrate with fleet management software.
Best Practices for Operation and Maintenance Operator Training and Certification
Provide in-depth training focusing on hand–eye coordination, sensor interpretation, and telemetric data usage. Encourage simulation drills that mimic real-world tasks.
Regular Calibration and Sensor Checks
Perform routine sweeps to align cameras, test LIDAR systems, and confirm that hydraulic sensors match pressure readings with workload demands.
Remote Diagnostics and Preventive Maintenance
Use telematic systems to track usage hours, hydraulic fluid conditions, and engine parameters. Schedule maintenance proactively to prevent breakdowns on remote or critical-job sites.
Safe Docking and Hand-Off Protocols
When transitioning control zones or recharging power systems, follow strict hand-off procedures. Operators must confirm safety zones, emergency-stop readiness, and re-sync of control latency settings.
Future Trends in Robotic Excavation Technology
Increased Autonomy
Semi-autonomous tasks—like trench digging or grading—are gaining traction. AI-driven excavation platforms can follow pre-programmed paths, reducing operator fatigue.
Electric and Hybrid Systems
As electric excavators become viable, expect quieter, greener operations with lower emissions and streamlined remote-control integration.
Advanced Human–Machine Interfaces
Emerging innovations include gesture recognition, voice commands, and immersive heads-up displays that overlay real-time excavation metrics directly into the operator’s view.
Fleet-Wide Optimization
Cloud-based analytics platforms now aggregate performance across remote units, enabling predictive scheduling, maintenance forecasting, and adaptive automation workflows.
Excavator Technology Comparison Table
| Feature / Type | Remote Control Excavator | Traditional Excavator | Autonomous Excavator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operator Location | Offsite or nearby with live visual feed | Inside machine cab | No direct operator (AI-controlled) |
| Control Method | Wireless joystick, touchscreen, VR | Manual levers and pedals | Pre-programmed AI or GPS-guided |
| Safety in Hazardous Zones | High | Low | High |
| Human Supervision | Required | Required | Optional |
| Real-Time Feedback | Telemetric and visual | Visual only | System diagnostics |
| Use Case Suitability | Confined spaces, demolition, mining | General earthmoving and construction | Repetitive large-scale excavation |
| Setup and Training | Moderate learning curve | Familiar to most operators | Requires tech support and planning |
| Maintenance Complexity | High due to sensors and electronics | Lower | High with software updates |
| Initial Cost | Higher upfront | Affordable baseline | Most expensive |
| Integration with Fleet Management | Advanced (telematics ready) | Limited | Fully integrated |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: How far can a remote control excavator operate from its operator?
A: Most units support reliable operation within 300–500 meters via line-of-sight radio; cellular or satellite links can extend range to several kilometers when network conditions allow.
Q: Are remote excavators more expensive than traditional ones?
A: While the upfront cost is higher due to teleoperation kits and sensors, long-term savings in safety, reduced labor, and minimal downtime often offset initial investments.
Q: Can remote excavators be retrofitted to existing models?
A: Yes—many suppliers offer retrofit kits that include remote control modules, cameras, and safety sensors. Compatibility depends on the model and hydraulic system architecture.
Q: What safety standards apply to remote-controlled construction equipment?
A: International and regional standards like ISO 16363 address teleoperation safety. Industry bodies also recommend redundant control systems, visual verification protocols, and regular audits.
Q: Do remote excavators require special licenses to operate?
A: Regulations vary by region. Some jurisdictions equate teleoperation with traditional operation, requiring the same operator certifications, while others treat it as specialized equipment with its own licensing rules.
Conclusion
Remote control excavators are transforming the landscape of heavy-duty construction and excavation by delivering exceptional safety, precision, and operational efficiency. With smart hydraulic control systems, real-time telemetric feedback, and next-gen operator interface designs, remote robotic diggers enable bold new approaches to complex or hazardous tasks. Whether you’re managing demolition, mining, or urban infrastructure work, investing in Remote Control Excavator technology can unlock unparalleled control at a distance.
TECH
Spark Plug & Wire Replacement: What’s the Real Cost?

When your engine starts misfiring or idling roughly, many mechanics suggest it could be time for a spark plug and wire replacement. But how much should you expect to pay for high‑tension leads, ignition coil inspection, and professional labor? In this guide, we break down the actual cost of replacing plugs and wires—covering parts, labor, performance considerations, and smart ways to save.
Understanding Spark Plugs and Ignition Wires
Spark plugs are essential components that deliver high-voltage electricity into the combustion chamber, igniting the fuel-air mixture. They consist of a central conductor, insulator, and shell that seals the cylinder head under extreme heat and pressure . Meanwhile, spark plug wires—also called high-tension leads—transfer the electrical spark from the ignition coil to the plug, often insulated with silicone or EPDM rubber to prevent RFI (radio frequency interference) .
Modern vehicles may use coil-on-plug systems that eliminate spark plug wires, but many older or economy models still rely on them. Whether you’re dealing with copper, platinum, iridium plugs, or silicone-insulated wires, the type and quality of these ignition components significantly influence both performance and cost.

Parts Cost Breakdown: From Copper to Iridium
Spark Plug Pricing
- Copper plugs are the most budget-friendly option, costing around $2–$10 each .
- Silver variants hover at approximately $5 apiece .
- Platinum and double-platinum upgrades run between $10–$20 each.
- Iridium plugs, known for their longevity and performance, range from $20–$100 per plug .
If your car has a V6 or V8 engine—or dual plugs per cylinder—the parts cost increases accordingly.
Ignition Wire Kit
A complete set of spark plug wires, including durable silicone insulation and high-quality connectors, usually costs $30–$150, depending on the brand and specs . High-performance or OEM-grade wires may exceed this range.
Additional Components
In some cases, mechanics recommend replacing related ignition system parts: faulty ignition coils can cost $150–$400 each . Dielectric grease is also commonly applied to boot ends to enhance sealing and prevent moisture-induced issues .
Labor Costs: Shop Time vs DIY
Professional Labor
Labor can range from $40 to $350 per hour, depending on engine complexity and access .
- On simpler 4‑cylinder layouts, it may take 1 hour—around $40–$150.
- For V6, V8, or tightly-packed turbo engines, labor can climb, especially if intake manifolds or coil packs must be removed .
Estimates often place total billable time between 1–2 hours, which equates to $70–$300 in labor .
DIY Route
Choosing parts and installing them yourself saves labor but requires tools (spark plug socket, torque wrench, gap gauge). Kits and tools may total $70–$600, depending on plug types and whether you already own tools .
Combined Cost Overview
When parts and labor are combined, typical replacement costs fall into these ranges:
| Scenario | Parts | Labor | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Economy 4‑cyl, copper plugs + wires | $20–$50 | $40–$100 | $60–$150 |
| Mid-range, platinum/iridium | $100–$300 | $70–$200 | $170–$500 |
| Performance V6/V8, high-end plugs | $200–$400+ | $150–$350 | $350–$750+ |
Some luxury or complex engines—with sealed heads or dual plugs—can run as high as $1,000–$1,300, particularly at dealerships .
Real‑Driver Experiences: Marketplace Insights
On Reddit, drivers often report surprise at high dealership quotes:
These anecdotes highlight how markup and labor escalation—especially at franchised dealers—can inflate costs.
What Influences Final Cost?
- Vehicle Make & Engine Layout
Tight engine bays add complexity—and time. - Plug Material & Brand
High-tension iridium or OEM parts cost more but outlast cheaper alternatives. - Labor Rates & Shop Type
Dealerships can double independent or regional shop rates. - Bundle vs. Single-Service
Combining plug and wire changes or adding coil replacement may be more economical in one visit.
DIY vs. Professional: A Comparison
DIY Advantages
- Saving potentially $100–$300 per job.
- Control over parts quality—buying reputable NGK, Denso, or Bosch plugs, or applying dielectric grease properly .
DIY Caveats
- Some installations (e.g. on Subaru flat-fours or turbocharged engines) require manifold removal—trickier than expected .
- Without proper torque and gap, misfires, cross-threading, or loosened plugs may arise.
When to Hire a Pro
If your vehicle uses coil-on-plug systems, has delicate wiring harnesses, or you lack tools and mechanical confidence—professionals can ensure a clean installation and often scan/clear OBD codes as part of the service.
Maintenance Intervals & Performance Benefits
Most manufacturers recommend spark plug replacement every 30,000–100,000 miles, depending on plug type:
- 30k–40k for copper
- 60k for platinum
- Up to 100k–120k for iridium
Spark plug wires typically last 100,000–160,000 km (60k–100k miles), although heat and engine bay exposure may reduce lifespan .
Replacing worn plugs and wires can restore acceleration, prevent misfires, improve fuel economy, and reduce strain on other ignition components like ignition coils or the catalytic converter .

Cost‑Saving Tips
- Buy Parts Online
Use RockAuto, AutoZone (with trade discounts), or Amazon—but beware of counterfeit items . Focus on trusted brands. - Bring Your Parts to the Shop
Many independent mechanics will install customer-supplied components—cutting dealership-style markup . - Bundle Services
Combine plug replacement with a tune-up or coil inspection to reduce redundant labor charges.
FAQs
Q: How much should it cost to replace plugs and wires?
A: On average, full service runs $100–$500, depending on vehicle and quality of parts .
Q: When is it time to change spark plug wires?
A: Rough idling, misfires, check‑engine light, or arcing w/ visible carbon streaks on boot ends are common signs .
Q: Do I need to replace wires with the plugs?
A: Ideally yes—mismatched new plugs with worn wires can undermine performance and efficiency.
Q: Can I replace them myself?
A: Yes—if you’re mechanically capable and have tools. But complex engines may require professional removal of manifold parts .
Q: Are iridium plugs worth it?
A: They cost more up front but last significantly longer—up to 100,000 miles—and resist carbon fouling, improving longevity and performance.
Conclusion
Spark Plug & Wire Replacement What’s the Real Cost? It varies—budget drivers may spend $100–$200, while complex engines or premium services can reach $750 or more. The total depends on plug material (copper, platinum, iridium), ignition wire quality, labor rates, and whether it’s an easy 4‑cyl or tight engine layout. DIY can save money, but mistakes can be costly. The smart approach? Use trusted parts, shop around, consider independent mechanics, and stick to your vehicle’s maintenance schedule.
-

 BLOG4 weeks ago
BLOG4 weeks agoSending Audio on Signal: Quick Guide
-

 TECH3 weeks ago
TECH3 weeks agoUsing AirTag with Android: Explained
-

 TECH3 weeks ago
TECH3 weeks agoAndroid No SIM Error: Fast Fix Guide
-

 BLOG3 weeks ago
BLOG3 weeks agoWoven Comfort: The Art of Furniture Fabrics
-

 BLOG2 weeks ago
BLOG2 weeks agoHow to Support a Loved One Dealing With Anger Challenges
-
 TECH3 weeks ago
TECH3 weeks agoAndroid System Intelligence: Smarter Tech Behind the Scenes
-

 BLOG4 weeks ago
BLOG4 weeks agoBuilt to Last: The Toughest Phones You Can’t Break
-

 TECH2 weeks ago
TECH2 weeks agoPower at a Distance: Mastering the Remote Control Excavator
