TECH
Discover the Powerful Impact of Applications of SIP Trunking Tech Target

Applications of SIP Trunking Tech Target (RDM) is a feature in VMware vSphere that allows a virtual machine (VM) to directly access a physical storage device, such as a LUN (Logical Unit Number) on a SAN (Storage Area Network). Instead of storing VM data in a virtual disk file (VMDK), RDM lets the VM interact with the storage hardware almost as if it were a physical server.
So, if you’re wondering, “What does RDM mean?” or “What is raw disk mapping?” here’s the simple answer: RDM is a way to map a physical storage device directly to a VM, bypassing some of the virtualization layers for specific use cases.
Why Use Raw Device Mapping in 2025?
You might be asking, “Why would anyone use raw device mapping when virtual disks are so easy to manage?” That’s a great question. In 2025, most workloads run perfectly fine on VMDKs, but there are still scenarios where RDM shines:
- Clustering: Some clustering solutions (like Microsoft Failover Clustering) require direct access to shared storage.
- SAN Features: If you need to use SAN-level snapshots or replication, RDM can provide the necessary access.
- Performance: In rare cases, RDM can reduce overhead and improve performance for high-I/O workloads.
- Physical-to-Virtual Migration: RDM can help during migrations where direct disk access is needed.
A virtualization engineer recently shared, “We use raw device mapping for our SQL cluster nodes. It’s the only way to get the shared storage access we need without sacrificing performance.”
Define RDM: The Technical Details
Let’s get a bit more technical. When you define RDM in VMware, you’re essentially creating a pointer file (the RDM file) in the VM’s datastore. This file doesn’t store data itself; instead, it points to the physical LUN. The VM then accesses the LUN directly, while VMware still manages permissions and snapshots at a high level.
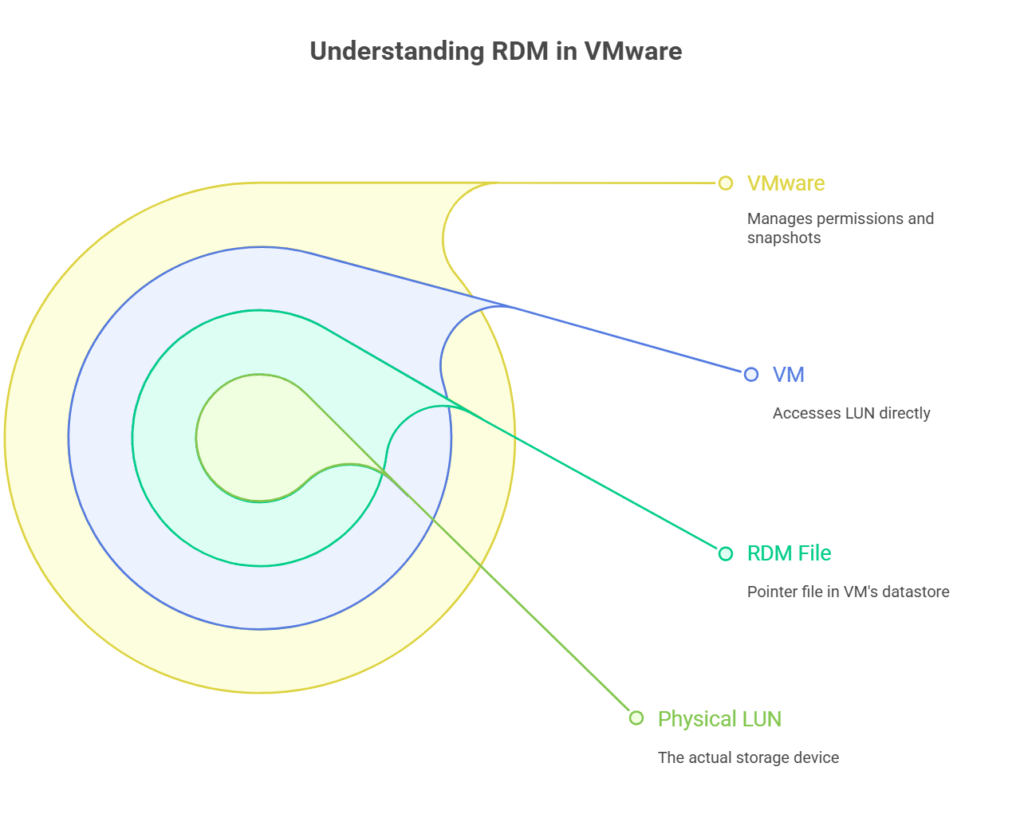
There are two types of RDM:
- Virtual Compatibility Mode: The RDM behaves like a VMDK, supporting features like snapshots and vMotion.
- Physical Compatibility Mode: The VM has almost direct access to the LUN, but some VMware features (like snapshots) are disabled.
What Is Raw Disk Mapping? (And How Is It Different?)
You might see the terms raw device mapping and raw disk mapping used interchangeably. In VMware’s world, they mean the same thing: mapping a raw, unformatted disk (or LUN) directly to a VM. The key difference from a regular virtual disk is that the VM can send SCSI commands directly to the storage device, which is essential for certain applications and clustering setups.
How Does Raw Device Mapping Work?
Here’s a step-by-step look at how RDM works in a typical VMware environment:
- Provision a LUN on your SAN or storage array.
- Create an RDM file in your VM’s datastore, pointing to the LUN.
- Attach the RDM to your VM as a new disk.
- Configure the VM to use the RDM for storage-intensive applications or clustering.
The VM now sees the raw device as if it were a physical disk, allowing for advanced storage operations.
Real-Life Example: RDM in Action
Let’s say you’re running a Microsoft SQL Server cluster in VMware. The cluster nodes need shared access to the same storage LUN. By using raw device mapping, you can present the same LUN to multiple VMs, enabling clustering features that wouldn’t work with standard VMDKs.
A sysadmin shared, “Without RDM, our SQL cluster simply wouldn’t work. It’s a lifesaver for legacy apps that need direct disk access.”
Pros and Cons of Raw Device Mapping
Pros
- Direct Storage Access: Enables advanced SAN features and clustering.
- Performance: Can reduce virtualization overhead for certain workloads.
- Flexibility: Useful for migrations and legacy applications.
Cons
- Complexity: More difficult to manage than standard virtual disks.
- Limited Features: Some VMware features (like snapshots) may not be available.
- Compatibility: Not all storage arrays or backup solutions support RDM.
RDM Meaning in Modern Virtualization
In 2025, the rdm meaning has evolved. While RDM is less common than it was a decade ago, it’s still a critical tool for specific scenarios. Most modern workloads use VMDKs for simplicity and flexibility, but RDM remains essential for:
- Clustering (Windows, Linux, Oracle RAC)
- SAN-level replication and snapshots
- Certain backup and disaster recovery solutions
What Does RDM Mean for Storage Performance?
One of the most common questions is, “What does RDM mean for performance?” The answer: it depends. For most workloads, the difference between RDM and VMDK is negligible. However, for high-I/O applications that need direct SCSI command access, RDM can offer a slight edge.
That said, advances in storage technology (like NVMe and all-flash arrays) have narrowed the performance gap. In 2025, the decision to use RDM is more about compatibility and features than raw speed.
When Should You Use Raw Device Mapping?
Here are the top scenarios where RDM makes sense:
- Clustering: When shared storage is required for failover or high availability.
- SAN Snapshots: If you need to leverage storage array features not available with VMDKs.
- Physical-to-Virtual Migrations: When moving legacy systems that require direct disk access.
- Specialized Applications: Some enterprise apps still require RDM for licensing or technical reasons.
When Should You Avoid Raw Device Mapping?
RDM isn’t always the best choice. Avoid it when:
- You don’t need direct access to the storage device.
- You want to use all VMware features (like snapshots, Storage vMotion, etc.).
- Simplicity and ease of management are top priorities.
How to Set Up Raw Device Mapping in VMware (2025 Edition)
Setting up RDM is straightforward, but it requires careful planning:
- Identify the LUN you want to map.
- In vSphere Client, right-click the VM and select “Edit Settings.”
- Add a New Hard Disk and choose “Raw Device Mapping.”
- Select the LUN and choose compatibility mode (virtual or physical).
- Complete the wizard and power on the VM.
Always consult your storage and backup vendors for compatibility before deploying RDM in production.
RDM vs. VMDK: Which Should You Choose?
| Feature | RDM (Raw Device Mapping) | VMDK (Virtual Disk) |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Storage Access | Yes | No |
| Snapshots | Limited (physical mode) | Yes |
| vMotion Support | Yes (virtual mode) | Yes |
| Ease of Management | More complex | Easier |
| Use Cases | Clustering, SAN features | General workloads |
What Is Raw Disk Mapping in Other Virtualization Platforms?
While VMware popularized RDM, other platforms have similar features. For example, Microsoft Hyper-V offers “pass-through disks,” and KVM/QEMU supports direct device mapping. The core idea is the same: give the VM direct access to a physical storage device.
RDM and Backup/Disaster Recovery
One of the biggest challenges with RDM is backup and DR. Not all backup solutions support RDM, especially in physical compatibility mode. Always verify your backup software’s capabilities before deploying RDM in production.
RDM in the Cloud Era: Is It Still Relevant?
With the rise of cloud-native storage and hyperconverged infrastructure, you might wonder if RDM is still needed. In 2025, most cloud workloads use virtual disks, but on-premises environments with legacy apps or strict compliance needs still rely on RDM.
What Does RDM Mean for Compliance and Security?
Direct disk access can raise compliance and security questions. Make sure to:
- Restrict access to RDM LUNs at the storage array level.
- Monitor and audit access to sensitive data.
- Use encryption and secure protocols where possible.
Real-World User Quote
“I thought RDM was old-school, but for our Oracle RAC cluster, it’s the only way to get the performance and reliability we need. Sometimes, the classic tools are still the best.”
FAQs
Q. What is raw device mapping and when should I use it?
A. Raw device mapping (RDM) lets a VM access a physical storage device directly. Use it for clustering, SAN features, or when an application requires direct disk access.
Q. What does RDM mean in VMware?
A. In VMware, RDM is a mapping file that points to a physical LUN, allowing the VM to interact with the storage device as if it were a physical server.
Q. What is the difference between RDM and VMDK?
A. RDM provides direct access to storage, while VMDK is a virtual disk file managed by VMware. RDM is used for special cases; VMDK is used for most workloads.
Q. Is raw device mapping still relevant in 2025?
A. Yes, especially for on-premises environments with clustering, SAN features, or legacy applications. However, most modern workloads use virtual disks for simplicity.
Best Practices for Raw Device Mapping in 2025
- Plan Ahead: Only use RDM when necessary.
- Document Everything: Track which VMs use RDM and why.
- Test Backups: Ensure your backup solution supports RDM.
- Monitor Performance: Watch for bottlenecks or issues.
- Stay Updated: Follow VMware and storage vendor recommendations.
Final Thoughts
In 2025, raw device mapping remains a powerful tool for specific use cases, even as virtualization and cloud technologies evolve. If you need direct storage access, advanced SAN features, or support for legacy clustering, RDM is still your best bet.
TECH
Soft Copy Meaning: Powerful Digital Advantage

Soft Copy Meaning refers to any document, image, or file that exists in a digital format. Unlike a hard copy, which is a physical printout you can touch and hold, a soft copy is stored electronically—on your computer, smartphone, tablet, or in the cloud.
Why does this matter? Because soft copies are the backbone of modern communication, collaboration, and record-keeping. Whether you’re emailing a contract, sharing a presentation, or submitting an assignment, you’re almost always dealing with a soft copy.
What Is a Soft Copy? The Simple Definition
What is a soft copy? It’s a digital version of any document or file. This could be:
- A Word document saved on your laptop
- A PDF emailed to your boss
- A photo stored on your phone
- An eBook downloaded to your tablet
- A spreadsheet in Google Drive
If you can view, edit, or share it electronically, it’s a soft copy.
Soft Copy vs Hard Copy: What’s the Difference?
The debate of hard copy vs soft copy is as old as the personal computer. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Feature | Soft Copy | Hard Copy |
|---|---|---|
| Format | Digital (PDF, DOCX, JPG, etc.) | Physical (paper, printout) |
| Storage | Computer, phone, cloud | Filing cabinet, desk |
| Editing | Easy, unlimited | Requires reprinting |
| Sharing | Instant (email, cloud, USB) | Mail, hand delivery |
| Eco-friendly | Yes (no paper used) | No (uses paper/ink) |
| Security | Can be encrypted, password-protected | Can be locked away |
In 2025, soft copies are the default for most businesses, schools, and even government agencies.
Real-World Example: Soft Copy in Action
A job seeker recently shared,
“I used to print out dozens of resumes for every interview. Now, I just email a soft copy or upload it to the company’s portal. It’s faster, cheaper, and I can update it anytime.”
This shift from hard copy to soft copy is happening everywhere—from job applications to legal contracts and beyond.
Why Are Soft Copies So Popular in 2025?
Several trends have made soft copies the standard:
- Remote work: Teams need to share and edit documents from anywhere.
- Cloud storage: Services like Google Drive and Dropbox make it easy to store and access files.
- Sustainability: Reducing paper use is good for the planet and your budget.
- Speed: Soft copies can be sent, received, and updated in seconds.
Types of Soft Copies: More Than Just Documents
When people think of soft copies, they often picture Word docs or PDFs. But the term covers a wide range of digital files:
- Text files: DOCX, TXT, PDF
- Spreadsheets: XLSX, CSV, Google Sheets
- Presentations: PPTX, Google Slides
- Images: JPG, PNG, GIF
- Audio/Video: MP3, MP4, WAV
- eBooks: EPUB, MOBI, PDF
If it’s digital, it’s a soft copy.
How to Create a Soft Copy
Creating a soft copy is easier than ever:
- Type it: Use a word processor, spreadsheet, or presentation tool.
- Scan it: Use a scanner or your phone’s camera to digitize paper documents.
- Download it: Save files from the internet or cloud services.
- Convert it: Use apps to turn photos or scans into PDFs or other formats.
How to Share a Soft Copy
Sharing a soft copy is simple and fast:
- Email: Attach the file and hit send.
- Cloud link: Share a Google Drive, Dropbox, or OneDrive link.
- Messaging apps: Send files via WhatsApp, Slack, or Teams.
- USB drive: For offline sharing, copy the file to a flash drive.
Soft Copy Security: Risks and Best Practices
While soft copies are convenient, they come with security risks:
- Unauthorized access: Files can be hacked or shared without permission.
- Data loss: Accidental deletion or hardware failure can wipe out files.
- Phishing: Malicious files can be disguised as soft copies.
Best practices:
- Use strong passwords and encryption.
- Back up important files regularly.
- Be cautious with email attachments and downloads.
Hard Copy vs Soft Copy: When Do You Still Need Paper?
Despite the rise of soft copies, there are times when a hard copy is still required:
- Legal documents: Some contracts or certificates need a physical signature.
- Official records: Certain government or medical forms may require paper.
- Archiving: Some organizations keep hard copies for long-term storage.
But even in these cases, a soft copy is often created first and then printed as needed.
Soft Copy in Education: The New Normal
In schools and universities, soft copies have transformed learning:
- Assignments: Students submit essays and projects online.
- E-books: Textbooks are now digital, saving money and weight.
- Collaboration: Group projects happen in Google Docs or Microsoft Teams.
A teacher shared,
“I can grade assignments from my tablet, leave comments, and return soft copies instantly. No more lost papers or late submissions.”
Soft Copy in Business: Efficiency and Flexibility
Businesses rely on soft copies for:
- Contracts and proposals: E-signatures make deals faster.
- Invoices and receipts: Digital records are easier to track and audit.
- Reports and presentations: Teams can collaborate in real time.
Soft Copy in Government and Healthcare
Even traditionally paper-heavy sectors are going digital:
- E-filing: Tax returns, permits, and applications are now online.
- Medical records: Patient files are stored and shared as soft copies, improving care and reducing errors.
Pros and Cons of Soft Copies
Pros
- Easy to edit and update
- Instant sharing and collaboration
- Eco-friendly and cost-effective
- Secure (with proper precautions)
- Takes up no physical space
Cons
- Requires devices and internet
- Vulnerable to hacking or data loss
- May not be accepted for all legal purposes
- Can be accidentally deleted or overwritten
Soft Copy Meaning in 2025: The Future Is Digital
Looking ahead, soft copies will only become more important:
- AI-powered search: Instantly find any document, image, or file.
- Blockchain verification: Ensure authenticity and prevent tampering.
- Universal e-signatures: Make soft copies legally binding worldwide.
- Augmented reality: View and interact with soft copies in 3D.
FAQs
Q. What is a soft copy?
A. soft copy is a digital version of a document, image, or file that can be viewed, edited, and shared electronically
Q. How is a soft copy different from a hard copy?
A. soft copy exists in digital form (like a PDF or Word doc), while a hard copy is a physical printout on paper.
Q. Can a soft copy be printed?
A. Yes! You can print a soft copy to create a hard copy whenever needed.
Q. Are soft copies secure?
A. Soft copies can be secure if you use strong passwords, encryption, and regular backups. Always be cautious with sharing and storing sensitive files.
Real-Life Example: Soft Copy Saves the Day
A small business owner lost her laptop to a coffee spill. Luckily, all her invoices and contracts were saved as soft copies in the cloud. She accessed them from her phone and kept her business running without missing a beat.
How to Organize and Manage Soft Copies
- Use folders and clear naming conventions
- Back up files to the cloud and an external drive
- Regularly delete outdated or duplicate files
- Use document management software for large collections
Hard Copy vs Soft Copy: Which Is Better?
For most uses in 2025, soft copies win on speed, convenience, and sustainability. But for legal, archival, or official purposes, hard copies still have their place.
Final Thoughts
Understanding soft copy meaning is essential in our digital world. From job applications to medical records, soft copies are everywhere—and knowing how to create, share, and secure them is a must-have skill.
TECH
Boost Your Security with Door Peephole Cameras: Top 3 Benefits

Have you ever wondered if your home’s security is truly up to par? With the rise of smart technology, the door peephole camera has become a must-have for anyone serious about safety. Whether you live in a bustling city apartment or a quiet suburban home, knowing who’s at your door—without opening it—offers peace of mind that’s hard to beat.
But what exactly makes a door peephole camera so effective? And how do you choose the right one for your needs in 2025? Let’s dive into everything you need to know, from the basics to the latest innovations.
Why a Door Peephole Camera is a Game-Changer
Traditional peepholes have been around for decades, but they come with limitations. You have to be physically present, and the view is often limited or distorted. Enter the door peephole camera—a modern solution that combines convenience, security, and smart features.
Imagine being able to see, record, and even communicate with visitors from your smartphone, no matter where you are. That’s the power of today’s peepholecams.
User quote:
“I travel a lot for work, and my peepholecam lets me check on my apartment anytime. It’s like having a security guard in my pocket.”
What is a Door Peephole Camera?
A door peephole camera is a compact device that replaces or enhances your traditional peephole. It captures video footage of anyone at your door and often includes features like motion detection, night vision, and two-way audio.
Some models, like the popular peepholecam, are designed specifically for renters and apartment dwellers. They’re easy to install and don’t require drilling or permanent changes to your door.
Key Features to Look for in a Peep Hole Camera
When shopping for a peep hole camera, consider these essential features:
High-Definition Video
Clear video is crucial for identifying visitors. Look for cameras with at least 1080p resolution.
Wide-Angle Lens
A wide field of view ensures you can see packages, pets, and anyone lurking just out of sight.
Motion Detection
Smart motion sensors alert you to activity at your door, even if the visitor doesn’t ring the bell.
Night Vision
Infrared LEDs allow you to see clearly, even in total darkness.
Two-Way Audio
Speak to visitors or delivery drivers without opening the door.
Easy Installation
Many peepholecams are designed for DIY installation, making them perfect for apartments.
Peepholecams vs. Traditional Door Cameras
You might be wondering: what’s the difference between a peepholecam and a standard door camera for apartment use?
- Peepholecams are typically smaller and designed to fit into existing peepholes.
- They’re less invasive, making them ideal for renters.
- Many models are battery-powered, so there’s no need for wiring.
On the other hand, traditional door cameras may require more installation work but often offer additional features like integrated doorbells or smart locks.
The Best Door Camera for Apartment Living
If you live in an apartment, security can be tricky. You want to protect your space without violating building rules or annoying your neighbors. That’s where a door camera for apartment use shines.
Look for models that:
- Don’t require drilling or permanent installation
- Offer cloud storage or local SD card recording
- Have discreet designs that blend in with your door
Real-life example:
A renter shared, “My landlord was fine with my peepholecam because it didn’t damage the door. Now, I feel safer, and my neighbors are thinking about getting one too!”
How to Install a Door Peephole Camera
Most modern door peephole cameras are designed for easy installation. Here’s a quick overview:
- Remove the existing peephole (if you have one).
- Insert the camera through the hole.
- Secure the device with the included hardware.
- Connect to Wi-Fi and set up the app on your phone.
No special tools or wiring required! If you’re unsure, many brands offer step-by-step video guides.
Privacy and Security: What You Need to Know
With any smart device, privacy is a top concern. Here’s how to keep your peep hole camera secure:
- Change default passwords immediately.
- Enable encryption if available.
- Regularly update firmware to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Review app permissions and only grant what’s necessary.
Pros and Cons of Door Peephole Cameras in 2025
Pros
- Enhanced security: See who’s at your door anytime, anywhere.
- Easy installation: Perfect for renters and homeowners alike.
- Smart features: Motion alerts, night vision, and two-way audio.
Cons
- Battery life: Some models need frequent charging.
- Wi-Fi dependency: No internet means no remote access.
- Privacy risks: As with any smart device, there’s a risk of hacking if not properly secured.
The Evolution of Peepholecams: What’s New in 2025?
The latest peepholecams are smarter than ever. Expect features like:
- AI-powered facial recognition
- Integration with smart home systems
- Cloud-based video storage with advanced encryption
- Voice assistant compatibility
These innovations make it easier than ever to keep your home safe and connected.
Real-World Uses: How People Are Using Door Peephole Cameras
From busy parents to frequent travelers, people are finding creative ways to use their door peephole cameras:
- Package delivery monitoring
- Checking on kids or elderly relatives
- Deterring porch pirates and unwanted solicitors
- Documenting suspicious activity for building management
FAQs
1. How does a door peephole camera work?
A door peephole camera replaces your traditional peephole, capturing video and sending it to your phone or a monitor. Many models offer motion detection and two-way audio.
2. Are peepholecams easy to install in apartments?
Yes! Most peepholecams are designed for renters and require no drilling or permanent changes.
3. Can I use a door camera for apartment security without Wi-Fi?
Some models offer local recording, but most smart features require Wi-Fi for remote access and alerts.
4. What’s the difference between a peep hole camera and a traditional doorbell camera?
Peep hole cameras are smaller, fit into existing peepholes, and are less invasive—making them ideal for apartments and rentals.
Final Thoughts
In 2025, the door peephole camera is more than just a gadget—it’s a smart investment in your safety and peace of mind. Whether you’re a renter, homeowner, or just someone who values privacy, there’s a model out there for you.
TECH
What Does a Transistor Do? Discover Its Powerful Role

What Does a Transistor Do? transistor is a tiny electronic switch or amplifier. It controls the flow of electrical current in a circuit, turning signals on or off, or making them stronger. This simple function is the foundation of all modern electronics—from your phone’s processor to the memory in your laptop.
User quote:
“I used to think transistors were just for engineers, but once I learned what a transistor does, I realized they’re the reason my phone, TV, and even my car work!”
The Transistor Symbol: Decoding Circuit Diagrams
If you’ve ever looked at a circuit diagram and wondered what those odd shapes mean, you’ve probably seen the transistor symbol. There are two main types of transistors: bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and field-effect transistors (FET). Each has its own symbol:
- BJT: Looks like a circle with three lines (emitter, base, collector) and an arrow.
- FET: A straight line with three connections (source, gate, drain) and a T-shaped symbol.
Understanding the transistor symbol is key to reading schematics and building your own circuits.
What Does a Transistor Do in a Circuit?
Transistors have two main jobs:
1. Acting as a Switch
A transistor can turn a current on or off, just like a light switch. In computers, billions of transistors work together to represent 1s and 0s—the language of digital logic.
2. Acting as an Amplifier
Transistors can also make weak signals stronger. This is how your phone’s microphone picks up your voice and sends it loud and clear to the other end.
What Does a Tdiagram Transistorransistor Do? (And Why the Confusion?)
You might have seen the phrase what does a tdiagram transistorransistor do floating around online. It’s a typo or a mashup of “transistor diagram” and “what does a transistor do.” But it’s a good reminder: understanding both the function and the diagram of a transistor is crucial for anyone learning electronics.
How Many Transistors in a CPU? (Prepare to Be Amazed)
One of the most mind-blowing facts about modern technology is how many transistors in a CPU. In 2025, a single high-end processor can have over 100 billion transistors packed into a chip smaller than your fingernail. That’s more switches than there are people on Earth—by a factor of ten!
This incredible density is what makes today’s computers, smartphones, and AI systems so powerful.
The Evolution of the Transistor: From Radios to AI
Transistors were invented in 1947, replacing bulky vacuum tubes. Early radios had just a handful of transistors. Today, your smartwatch has more computing power than the computers that sent astronauts to the moon—all thanks to the relentless miniaturization of transistors.
Real-World Example: Transistors in Everyday Life
Think about your morning routine. Your alarm clock, coffee maker, and smartphone all rely on transistors. When you unlock your phone, millions of transistors in the display, processor, and memory work together in a split second to show your notifications.
How Transistors Changed the World
Without transistors, there would be no laptops, no internet, no streaming music, and no electric vehicles. They’re the unsung heroes of the digital age.
Types of Transistors and Their Uses
1. Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)
Used in amplifiers, radios, and analog circuits.
2. Field-Effect Transistor (FET)
Common in digital circuits, computers, and memory chips.
3. MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor FET)
The workhorse of modern CPUs and memory.
How Do Transistors Work? (A Simple Explanation)
A transistor has three parts: input, control, and output. When a small current or voltage is applied to the control (base or gate), it allows a larger current to flow from input to output. This is how it acts as a switch or amplifier.
Transistor Symbol in Practice: Reading a Schematic
Let’s say you’re looking at a circuit diagram for a simple amplifier. You’ll see the transistor symbol connected to resistors and capacitors. The arrow shows the direction of current flow. Once you recognize the symbol, you can start to understand how the circuit works.
What Does a Transistor Do in a Computer?
In computers, transistors are the building blocks of logic gates. Billions of them work together to perform calculations, store data, and run software. Every time you open an app, stream a video, or play a game, you’re relying on transistors.
How Many Transistors in a CPU: The Numbers Keep Climbing
- 1970s: Thousands of transistors per chip
- 2000s: Millions per chip
- 2025: Over 100 billion per chip
This exponential growth is known as Moore’s Law, and it’s the reason technology keeps getting faster and more powerful.
Risks and Challenges: The Limits of Transistor Technology
As transistors get smaller, they become harder to manufacture and more prone to errors. Engineers are exploring new materials, 3D stacking, and even quantum transistors to keep progress going.
Pros and Cons of Transistors
Pros
- Tiny size: Enables compact, powerful devices
- Low power: Efficient and cool-running
- Fast switching: Billions of operations per second
Cons
- Complex manufacturing: Requires advanced technology
- Heat management: Billions of transistors generate heat
- Physical limits: Approaching the size of individual atoms
Transistors in 2025: What’s New?
- 3D transistors: Stacked layers for more power in less space
- AI-designed circuits: Machine learning helps optimize transistor layouts
- Flexible electronics: Transistors in wearable and bendable devices
How to Spot a Transistor in a Circuit
Look for the transistor symbol—a circle with three lines or a T-shaped symbol. It’s usually connected to other components like resistors and capacitors.
Real-World Example: A Tweet About Transistors
“Just learned that my phone has more transistors than the first supercomputers. Mind blown! #techfacts”
FAQs
Q. What does a transistor do in simple terms?
A. transistor acts as a switch or amplifier, controlling the flow of electricity in a circuit.
Q. What is the transistor symbol in a circuit diagram?
A. The transistor symbol is a circle with three lines (for BJT) or a T-shaped symbol (for FET), showing the connections and current flow.
Q. How many transistors in a CPU in 2025?
A. High-end CPUs in 2025 can have over 100 billion transistors, enabling incredible processing power.
Q. What does a tdiagram transistorransistor do?
A. This phrase is a typo, but it refers to understanding both the function and the diagram of a transistor in electronics.
Final Thoughts
Understanding what does a transistor do isn’t just for engineers. It’s the key to appreciating the technology that powers your life. From the transistor symbol in a circuit diagram to the staggering number of transistors in a CPU, these tiny devices are the foundation of the digital world.
-

 TECH3 weeks ago
TECH3 weeks agoSoft Copy Meaning: Powerful Digital Advantage
-

 BLOG1 month ago
BLOG1 month agoHeaven’s Touch: A Miracle Prayer for Healing
-

 HEALTH1 month ago
HEALTH1 month agoHormone Health for Men: Signs, Solutions, and Staying Proactive
-

 FASHION2 months ago
FASHION2 months agoStyle Your Tech: Custom HP Notebook Cover Skins for a Sleek Look
-

 BLOG1 month ago
BLOG1 month agoHow to Support a Loved One Dealing With Anger Challenges
-

 TECH2 months ago
TECH2 months agoBlue Android Phone: Single Camera Simplicity
-

 TECH2 months ago
TECH2 months agoAndroid No SIM Error: Fast Fix Guide
-

 BLOG2 months ago
BLOG2 months agoSending Audio on Signal: Quick Guide
